Patient-Reported Changes in Weight, Appetite, and Lifestyle During Evolocumab Therapy
Keywords:
Evolocumab, PCSK9 inhibitors, weight loss, dyslipidemia, weight gainAbstract
Abstract
Background
Evolocumab is a PCSK9 inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy in lowering LDL-C levels and in reducing cardiovascular event risk. Even though initial clinical trials have not consistently reported weight change as an adverse effect, anecdotal patient reports show potential changes in body weight associated with its use.
Objective
To assess patient-reported changes in body weight, appetite, and lifestyle behaviors after initiation of evolocumab using an anonymous online questionnaire.
Methods
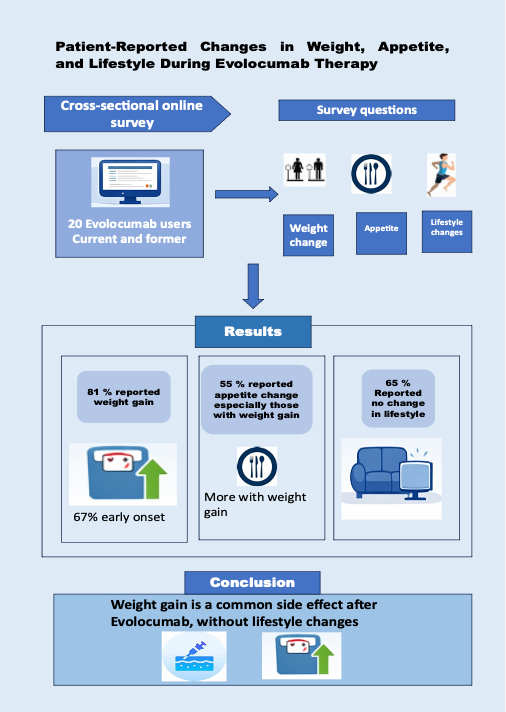
It was a cross-sectional, online survey carried out among self-identified current or former users of evolocumab. Participants completed a survey questionnaire regarding weight changes and their timing, appetite, lifestyle modifications, and subjective effects of the drug. Their responses were summarized by using descriptive statistical methods; 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were measured for each proportion, and Fisher’s exact test was later applied for comparing subgroups.
Results:
After initiating evolocumab, 19 (90%; 95% CI 68–99%) out of 20 respondents conveyed weight changes. Seventeen participants (81%; 95% CI 59–95%) reported weight gain, while 4 (19%; 95% CI 5–41%) experienced weight loss. Weight changes were observed within the first few weeks by 14 individuals (67%; 95% CI 43–85%). Regarding lifestyle behavior, most participants (13/20; 65%) did not perceive any change. Sixteen respondents (84%) noticed a significant impact of evolocumab on their weight, with perceived impact more frequent among those reporting weight gain (88% vs 25%, p = 0.02). 11 respondents (55%) conveyed appetite changes, especially those who disclosed weight gain (59% vs 25%, p = 0.3).
Conclusions:
An exploratory online survey indicated weight gain after initiating evolocumab, usually early during therapy, and was independent of lifestyle changes. These results highlight the relevance of patient-perceived drug effects on quality of life. This survey supports conducting the prospective studies to evaluate weight-related effects of PCSK9 inhibitors.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this case report are included in this published article. No additional datasets were generated or analyzed.
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Diabesity

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
All articles published in the Journal of Diabesity (JOS) are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
What this means:
Under the CC BY 4.0 license, authors retain copyright of their work, while allowing others to:
-
Share — Copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
-
Adapt — Remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially
Conditions:
Users must provide appropriate attribution to the original author(s) and source, including:
-
The article title
-
Author(s) name(s)
-
Journal name (Journal of Diabesity)
-
DOI or link to the original article
-
An indication if changes were made
There is no restriction on commercial use or derivative works, as long as proper attribution is given.
Full License Text:
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
✍️ Author Rights:
-
Authors retain copyright and grant JOS the right of first publication.
-
Authors may archive the published version in institutional repositories, personal websites, or other platforms with proper citation.





